RoboVoyager
Your interface to the robot
About
In the world of teleoperations, being able to remotely control robots, as well as monitor their sensors and other various data, is a must. This interface makes it easy for the users to do so
How it Works
Make sure the connection is established by connecting to the robot's network and IP from your phone or computer. In the Robot page, you can toggle features on or off by clicking on their buttons
Features
Controls
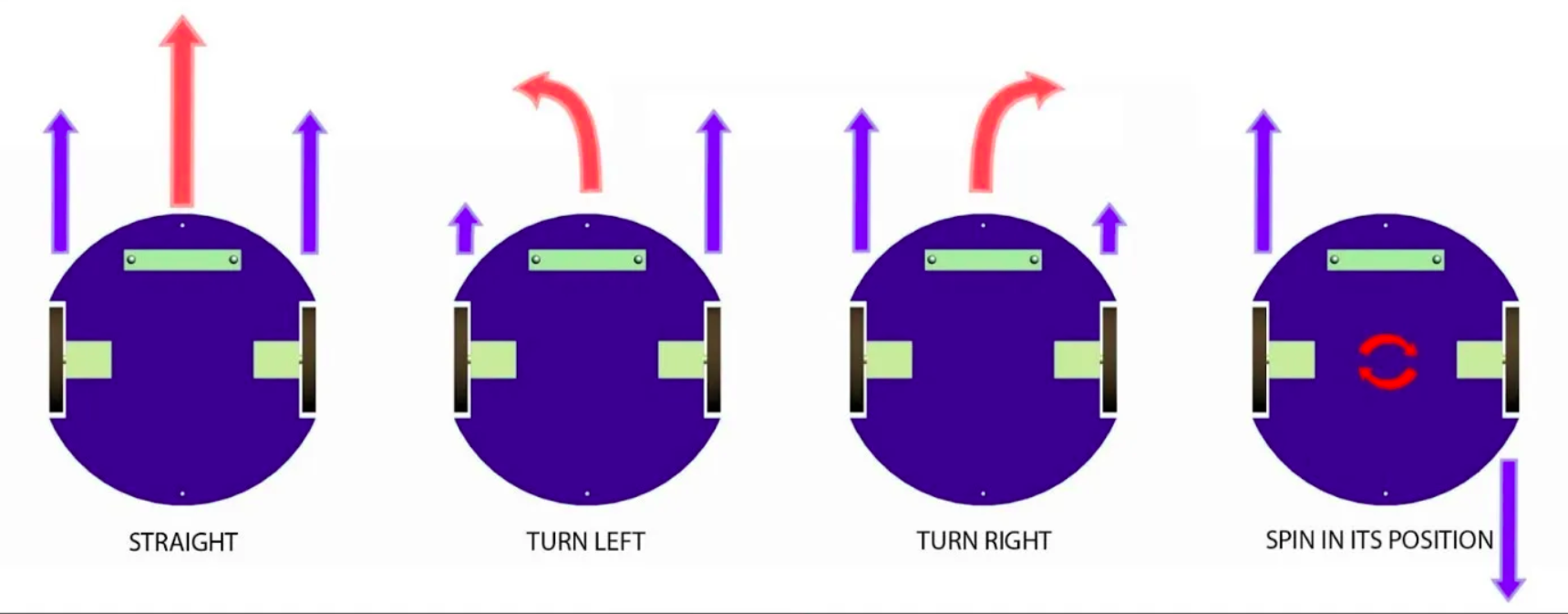
A Virtual Joystick is provided to remotely control the robot. It sends a vector of movement
to the robot by publishing it to the /cmd_vel (command velocity) topic. There
are 8 possible directions, including moving diagonally. RoboVoyager is a
differential robot, so one
wheel's speed is "differentiated" from the other and that's how it can rotate around and move
in a curvy line
Video Streaming
When a user is remotely controling a robot over a distance, a video stream is essential.
Video streaming is offered at a low resolution for faster viewing speed. Raw camera footage
is first resized and then converted into JPGs. Robot's computer only sends data after a user
subscribes to the /video_streaming topic
Sensors
Monitor sensor data from the robot. The most useful ones are battery levels and upload rate during video streaming
Data Saving
Save and analyze collected data for later. Data saver node collects information from Lidar, GPS, and Zed2 camera (but the camera has many more sensors built inside it). Be cautious of prolonged use, as 10 seconds fills up around 100 MBs
Other projects
Moborobot
This project was about making the robot go from point A to point B, by using Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) and object avoidance algorithm
Moborobo GMapping
This project is an upgraded version of Moborobot. Navigating from point A to point B now works without mapping prior area, but tiles of an offline map are still necessary as a general overview of the area, and designating destinations